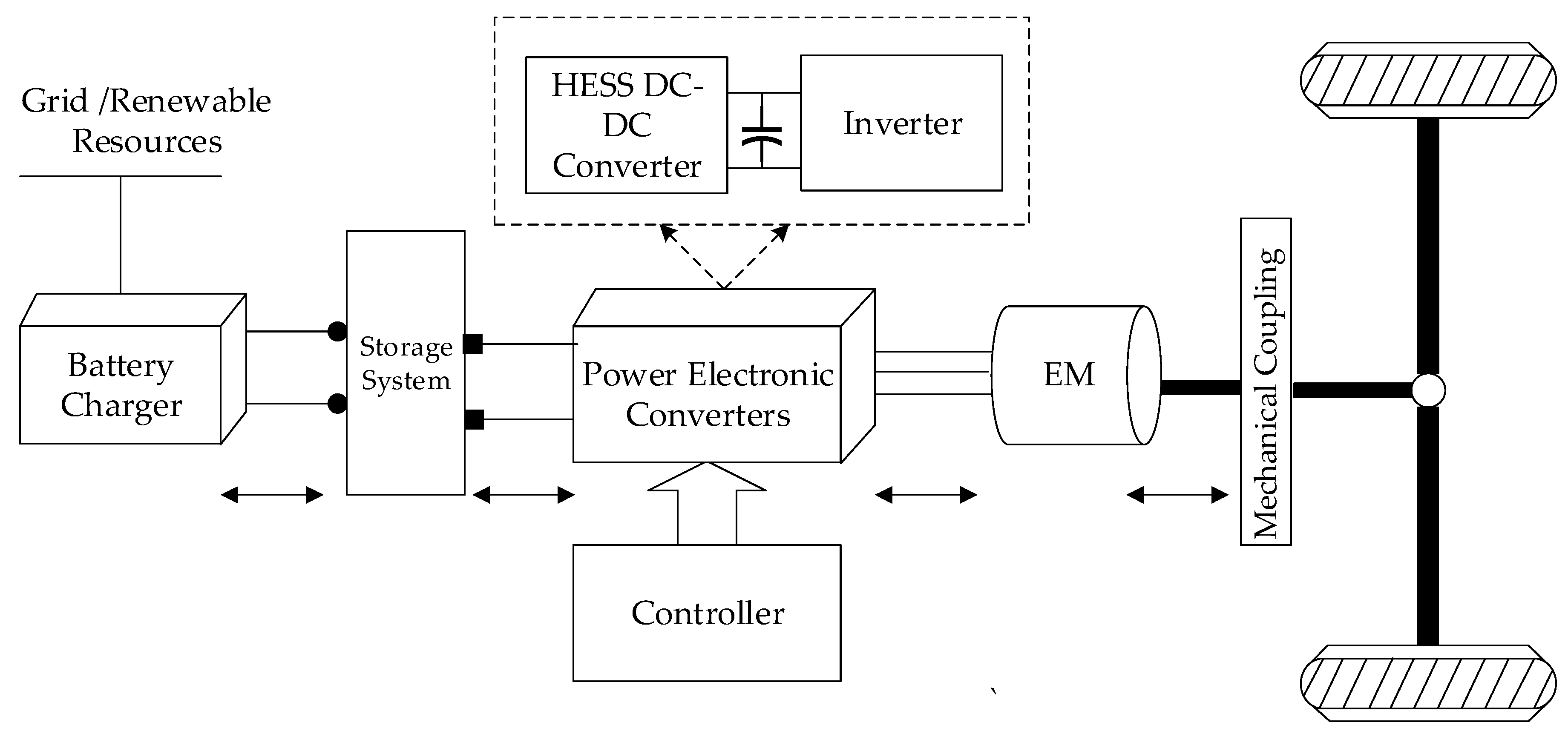
The block diagram of an electric vehicle (EV) typically illustrates the essential components and their interconnections. It showcases how energy flows from the battery to power the electric motor and drive the vehicle.
Exploring the electrification of transportation leads us to electric vehicles, a sustainable alternative to conventional internal combustion engine cars. At the heart of an electric vehicle lies its battery pack, which stores electrical energy for use by the motor. The electric motor, the driving force behind the wheels, converts electrical energy into mechanical power.
A meticulous arrangement of onboard chargers, inverters, and controllers manage this energy conversion and flow, ensuring efficient operation. Key ancillary systems, such as regenerative braking, play a dual role in both deceleration and energy recuperation. By integrating connectivity and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), EVs also pave the path towards a smarter automotive future. This evolution is crucial for reducing our carbon footprint and progressing towards cleaner transportation options.
Electric Vehicles Unplugged
Imagine a future with clean air and quiet streets. Electric vehicles (EVs) are leading the way. EVs use electricity to run. They do not need gasoline. This means they do not pollute the air much. People want to save the planet. So, they are choosing electric cars more often. Let’s explore the magic inside these cars.
The Rise Of The Electric Vehicle
Electric cars are becoming popular. Many countries support them. They offer tax savings for buyers. Car companies are making more electric models. Everyone sees EVs as a smart choice.
Key Components Powering The Electric Revolution
- Battery Pack: This is the heart of the EV. It stores electricity. It powers everything.
- Electric Motor: The motor turns the wheels. It is very strong and silent.
- Onboard Charger: This changes the power. It helps the battery charge from your home.
These components work together. They make the car move without any smoke.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Peeking Into The Heart: The Block Diagram Essentials
Understanding the inner workings of an electric vehicle (EV) starts by looking at a block diagram. This visual guide reveals the various components and how they connect, making it easier to comprehend the complex systems that power EVs. We’re diving into these diagrams and uncovering the core elements of electric vehicles.
Simplifying The Complex: What Is A Block Diagram?
A block diagram is a simplified illustration. It shows systems as blocks linked by lines. These lines represent connections or data paths. It’s like a map of an EV’s system, giving a clear, high-level view.
Basic Building Blocks Of Electric Vehicles
An electric vehicle’s main components show the leap from traditional to electric automotive design. Here’s a quick list of what powers these futuristic machines:
- Electric Motor: Turns electricity into movement.
- Battery Pack: Stores energy for the motor.
- Inverter: Adjusts electric currents.
- Onboard Charger: Refills the battery from an external source.
- DC/DC Converter: Changes voltage levels.
- Thermal System: Manages temperature for efficiency.
- Power Electronics Controller: Directs the flow of electrical energy.
- Transmission: Delivers motor power to the wheels.
- Regenerative Braking System: Recovers energy during stops.
Propulsion Powerhouse: Electric Motor And Battery Pack
The heart of an electric vehicle lies in its Propulsion Powerhouse: the electric motor paired with a high-performance battery pack. This duo drives the wheels, offering a clean, efficient, and powerful ride.
Electric Motor Mechanics
At the core of at an electric vehicle’s propulsion system is the electric motor. It converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, which turns the wheels. Unlike conventional engines, electric motors deliver torque instantly for quick acceleration.
- AC Induction Motors: No brushes, less maintenance.
- Permanent Magnet Motors: Greater efficiency, smaller size.
- Switched Reluctance Motors: Simple design, cost-effective.
Battery Technology And Management Systems
The battery pack is not just a single component. It’s a complex system designed for optimal performance and safety. The pack includes multiple lithium-ion cells, managed and protected by an advanced Battery Management System (BMS).
The BMS monitors and regulates battery health by checking voltage, current, and temperature. This prevents damage and extends battery life. Batteries also use thermal management systems to maintain optimal temperature.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cathode | Conducts positive charge. |
| Anode | Conducts negative charge. |
| Electrolyte | Allows ion flow. |
| Separator | Prevents short circuits. |

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Bringing It All Together: Energy Flow And Control Systems
Electric vehicles (EVs) are marvels of modern technology. They bring together various components. These parts work in unison. This allows EVs to operate efficiently. In this section, we explore the energy flow and control systems in EVs. We will see how all parts connect. We will understand how they create a seamless driving experience.
Energy Conversion Processes
Electric vehicles convert energy from one form to another. This is a key function. It ensures the car can drive. Let’s delve into these processes:
- Chemical to Electrical: The battery stores chemical energy. When you drive, this changes to electrical energy.
- Electrical to Mechanical: The motor takes electrical energy. It turns it into mechanical energy. This pushes the car forward.
- Regeneration: When slowing down, the car takes mechanical energy. It changes it back to electrical energy. This recharges the battery a bit.
Control Units And Drive Electronics
The heart of an EV’s system lies in its control units. These are the brains of the operation. They manage how energy moves and directs the drive electronics. Below we highlight their roles:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery Management System (BMS) | It watches the battery’s health. It keeps it safe. |
| Motor Controller | It controls the motor’s speed. It also controls torque. |
| Power Electronics | They shape the electrical energy. They make it right for the motor. |
Together, these control systems handle complex tasks. They keep everything running smoothly. By thorough monitoring and quick adjustments, they ensure the best performance.
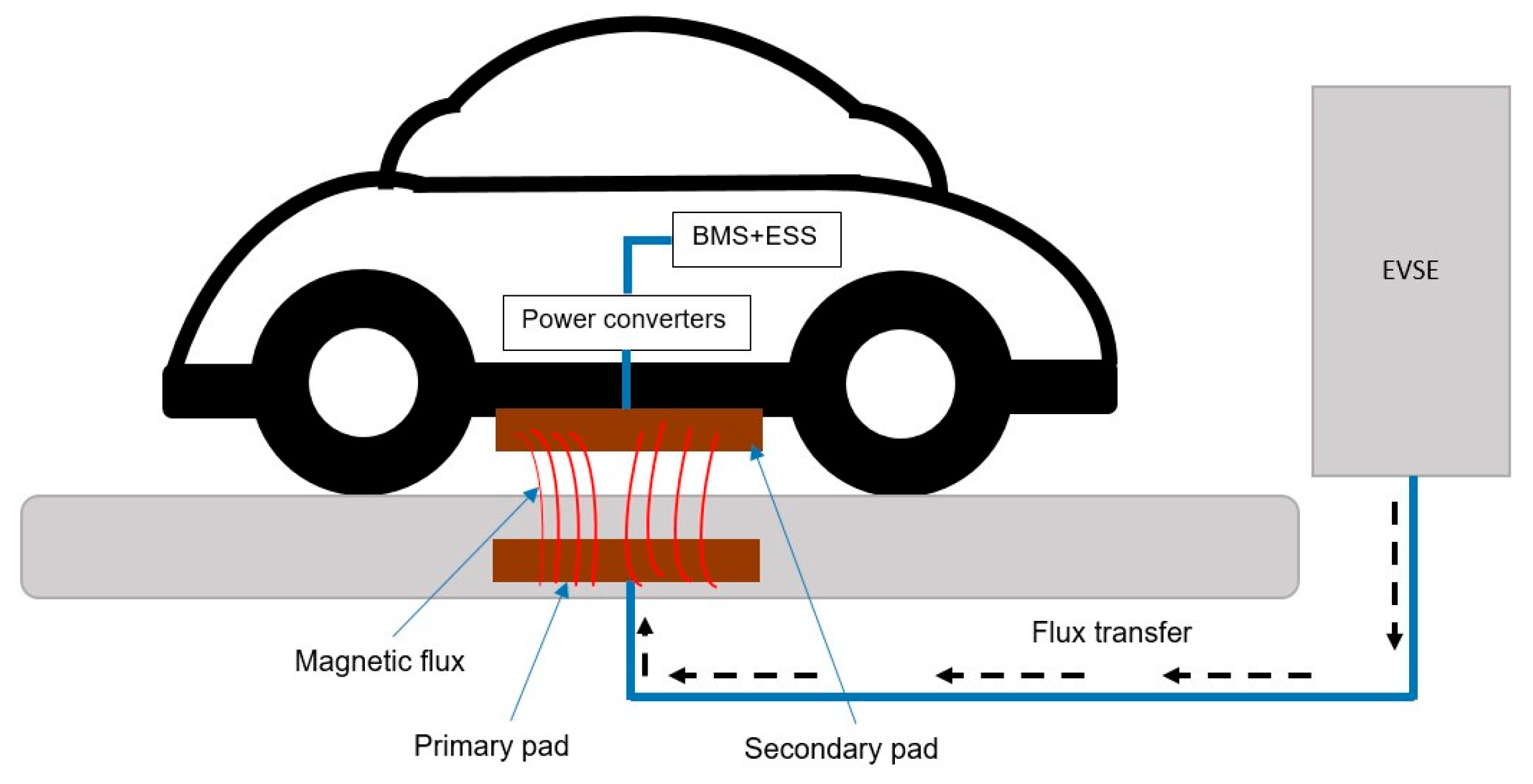
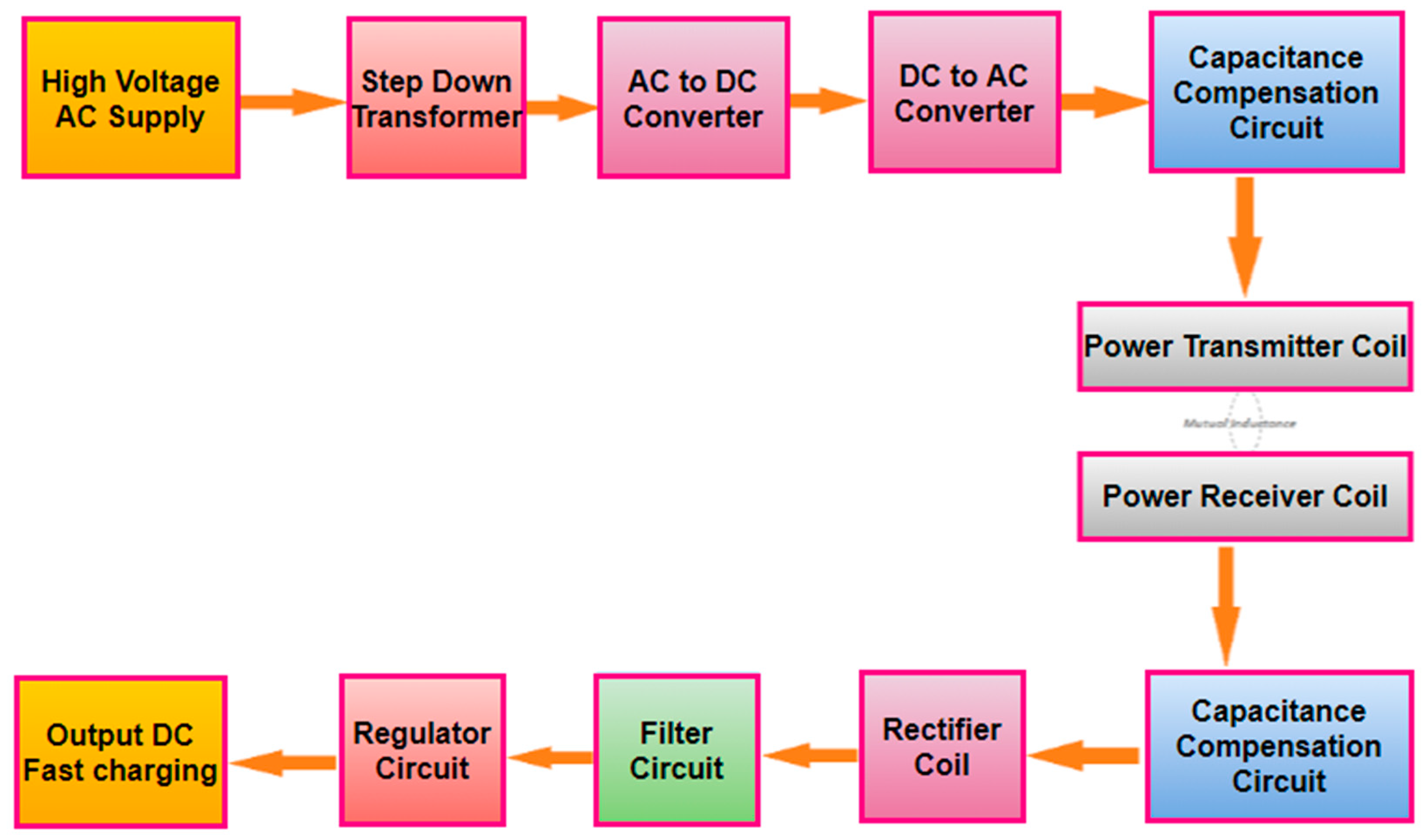
Charging Up: Ev Charging Systems
The heart of Electric Vehicles (EVs) pulses with electrons. Their lifeblood comes from efficient and reliable charging systems. Understanding how these systems recharge an EV’s battery is crucial. It enhances performance and overall user experience. Let’s explore the different types of EV chargers and their integration within vehicle systems.
Types Of Ev Chargers
- Level 1 Chargers: These plug into standard household outlets. They offer slow charging, perfect for overnight use.
- Level 2 Chargers: They need special installations. Charge times are faster, making them suitable for home and public use.
- DC Fast Chargers: The quickest option available. They are ideal for on-the-go charging at public stations.
Each charger type serves a distinct purpose. Users choose based on their needs. Whether it’s a quick top-up or a full overnight recharge, there’s a solution.
Integration With Vehicle Systems
EV charging isn’t just about plugging in and waiting. It’s an advanced interaction between the charger and the vehicle. This integration ensures:
- Efficient Charging: The vehicle communicates with the charger to optimize the charging rate.
- Battery Health: Continuous monitoring protects the battery from overcharging.
- Smart Functions: Some systems allow remote control via apps.
The synergy between chargers and vehicle systems improves user convenience. It extends the battery life and supports remote charge management.
Future Trends: Emerging Technologies In Evs
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is rapidly evolving. New technologies are on the horizon. These advancements promise to improve performance and efficiency. Let’s explore some exciting future trends shaping the world of EVs.
Innovations In Electric Powertrains
Electric powertrains are the heart of EVs. They are getting smarter and more efficient. Below are key developments:
- Integrated systems that combine motors, controllers, and transmissions.
- Modular powertrains for easy customization and upgrades.
- Advances in regenerative braking to recover more energy.
Next-gen Battery Solutions And Energy Storage
Batteries are key to an EV’s range and performance. Innovations include:
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Solid-state batteries | Higher energy density and safety. |
| Lithium-sulfur batteries | More power, less environmental impact. |
| Wireless charging | Convenience and reduced charging times. |
Improved energy storage solutions are in development too. They will ensure longer drives without frequent stops for charging.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Block Diagram Of Electric Vehicle
What Is A Block Diagram In Electric Vehicles?
A block diagram in electric vehicles (EVs) represents the system’s primary components and their interconnections. It helps visualize the flow of electricity and signals, aiding in understanding the vehicle’s functional operations.
How Does An Ev Powertrain Work?
An EV powertrain includes the battery, motor, and controller. The battery provides power, while the motor converts it into mechanical motion. The controller manages the power flow, ensuring efficient vehicle operation.
Components Of An Ev Battery System?
The EV battery system comprises cells, modules, a battery management system (BMS), and thermal management components. The BMS oversees the system’s performance, ensuring safety and longevity.
What’s The Role Of An Inverter In Evs?
An inverter in EVs converts DC power from the battery to AC power, which then drives the electric motor. Its efficiency is critical for the vehicle’s overall performance and range.
Conclusion
Exploring the block diagram of an electric vehicle offers fascinating insights into the future of transportation. By dissecting its components, we gain a clearer understanding of the EV’s inner workings. Remember, embracing sustainable mobility begins with knowledge. Keep learning, keep innovating, and join the revolution towards a cleaner, greener planet.